
1. Preliminary preparation:
Patent Search: Before filing an application, it is essential to conduct a thorough patent search. The applicant should search existing patent literature, academic papers, relevant products on the market, etc., to ensure the Novelty and Noobviousness of the design. Patent search can be done using the USPTO's patent search tool or with the help of a professional patent agency.
Prepare the application materials: Prepare the complete application materials including:
Applicant and Inventor information: Fill in the name, address and other contact information of the applicant and inventor.
Design drawing: Clear and accurate design drawing is the core of design patent application. Drawings should show all the details of the design and provide views from different angles, including front view, rear view, side view, top view and bottom view.
Written description: A brief description of the features of the design, but generally design patents rely more on drawings to define the scope of protection.
2. Submit the application
Applicants are required to file a design patent application with the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) and pay the appropriate filing fee. Submissions can be made electronically (through the USPTO's electronic Application system, EFS-Web) and on paper. Electronic submission is more convenient and less expensive. Application documents include application forms, drawings, written descriptions, and application fees.
3. Formal review
The USPTO conducts a formal review of the submitted application documents to check whether the documents are complete, the format is correct, and the drawings are in compliance with regulations. The formal review is usually completed within a few weeks of submission. If a problem is found during the proforma review, the USPTO will issue a notice asking the applicant to make changes within a specified time frame.
4. Substantive review
Substantive examination is the core stage of design patent application. The examiner will conduct a detailed examination of the applied design to assess its novelty and uniqueness. The examiner searches prior art and compares the requested design with the known design. A substantive review usually takes between 12 and 24 months, depending on the workload of the examiner and the complexity of the case.
5. Review comments
If the examiner finds problems with the application during the substantive examination, such as a lack of novelty in the design or a lack of clarity in the description, an Office Action will be issued. The applicant is required to respond to the review within a specified time (usually three months), and may overcome the examiner's objections by revising drawings or descriptions and providing additional evidence. If the applicant fails to respond within the specified time, the application may be rejected.
6. Authorization and issuance
If the application is approved, the USPTO will issue a Notice of Allowance. The applicant shall pay the registration fee and complete the patent registration procedure within the specified time. Upon completion of registration, the USPTO will issue a formal patent certificate, granting the applicant the right to protection of the design patent.
7. Patent maintenance
The term of protection of a U.S. design patent is 15 years, counting from the date of registration of the patent. Unlike invention patents, design patents are not subject to maintenance fees during their protection period. This simplifies the maintenance responsibility of the patent holder and ensures that the patent rights continue to be valid throughout the protection period.
Based on the above steps, here is a simplified flowchart:
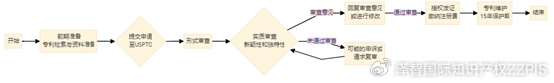
Through the above detailed process, you can see the various steps and key points in the process of applying for a design patent in the United States. The applicant should be fully prepared to ensure the quality of the design drawings and the integrity of the application materials to improve the probability of success of the application. In addition, understanding and responding to examination opinions is also a key link, and applicants can seek the help of professional patent agencies to cope with various challenges in the examination process.